Deinosuchus
One of the extinct relatives of alligators are the Deinosuchus. The Deinosuchus lived during he Late Cretaceous period, which was about 80 to 73 million years ago. Its name is derived from the Greek words, “terrible crocodile”.
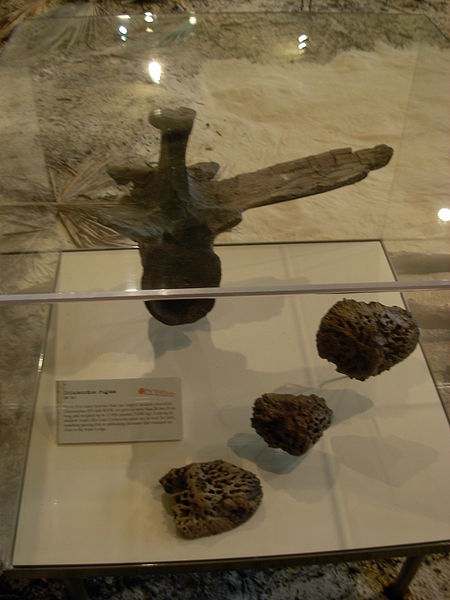
The remains of the Deinosuchus was first found in the 1850s in North Carolina, USA. However, it was not until 1909 that the genus of the Deinosuchus was actually described and named. This is because complete fragments were not yet recovered. More fragments were found in the 1940s and then incorporated into an influential skull reconstruction at the American Museum of Natural History, which was actually inaccurate. As no full skeletons of the Deinosuchus have been found, knowledge of this creature is incomplete. However, cranial material have been found in more recent years which has helped to expand the world’s scientific knowledge about this predator.
If you think today’s modern day alligators or crocodiles are scary, then you definitely would not want to face up to a Deinosuchus. This is because Deinosuchus’ measure up to about 12 metres long and weigh 8.5 metric tons. Its appearance is quite similar to its smaller-sized relatives. Its teeth were quite large and robust and were built for crushing its prey. Its back was covered with semi-spherical osteoderns. It is suggested that the Deinosuchus lived for only up to 50 years which is similar to modern day crocodiles.
Fossils of the Deinosuchus that have been found are mostly in the USA and in Mexico. Its habitat included the Western Interior Seaway. In this seaway, the Deinosuchus was an opportunistic predator at the top of the chain. It was the largest animal in its western habitat, but it is thought that in the eastern habitat, it had a larger population. It is also thought that the Deinosuchus was able to kill and eat large dinosaurs, and that it may have also eaten fish, sea turtles, and other prey both on land and in the water.